table of contents
Overview of Australian intellectual property law
competent authority
Australian Intellectual Property Office (IP Australia)
It is part of the Australian Federal Government's Department of Industry and has jurisdiction over patents, designs, trademarks and plant breeding rights.
Treaties related to industrial property rights to which Australia is a member
- treaty of paris
- Berne Convention
- Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT)
- WIPO Establishment Treaty (WIPO Treaty)
- Budapest Treaty on the International Recognition of the Deposit of Microorganisms
- Agreement Establishing the World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Hague Agreement on Exemption from Consular Certification of Foreign Official Records
- International Convention for the Protection of New Varieties of Plants (UPOV Convention)
- Nice Agreement on the International Classification of Goods and Services for the Registration of Marks
- Trademark Law Treaty
- Madrid Protocol Concerning the International Registration of Marks
Patent
Over 11,378% of patent applications in Australia result from the national phase of PCT applications. Looking at the annual number of applications in Australia by country, the United States has the largest number of applications (2,627), followed by Australia (1,746) and Japan (2012) (XNUMX IP Australia).
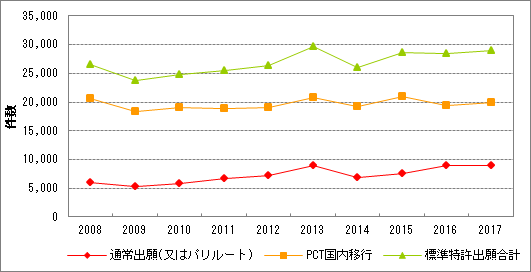
(From IP Australia 2012 statistics)
Type of patent
There are two types of Australian patents:
1.Standard patent
Standard patents are suitable for protecting more complex advanced technology inventions.
2.Patents of Addition
A patent of addition is granted when a patent for the "main invention" (main patent) has been filed or granted, and a new application is filed for an "improvement or modification" of the main invention. A patent of addition can be filed by the applicant for the main invention or by the same person as the patentee of the main patent.
Patents of addition are primarily useful for obtaining protection for improvements or modified embodiments developed after the filing of the main patent and not expressly claimed in the main patent.
-
- *Furthermore, there is a provisional patent application system, but a provisional patent application itself will not be granted a patent.
Application route
Applications can be made via the Paris route and the PCT route. In the case of the PCT route, the national phase entry procedure must be completed within 31 months from the priority date.
Documents required for application
- 1. Application, specification, claims, abstract, and necessary drawings
Documents must be written in English. - 2. Notice of Entitlement
If the applicant is not the inventor, this is a document explaining that the applicant has inherited the right to obtain a patent from the inventor. The local agent must sign and submit the application, so it is necessary to explain the succession to the local agent at the time of application. - 3. Priority certificate for Paris route
Protection target
The following items are covered by patent protection:
- Method of treatment
- software
- Business Model
- Product-by-process claims
Furthermore, "human beings and biological methods for their production" are excluded from protection (Article 18 (2) (3) of the Act).
Application publication
Standard patent applications are published 18 months after the filing date or the priority date, whichever is earlier. (Article 53 of the Act)
Examination
Standard patent applications are subject to substantive examination. Please note that the revised examination system has been abolished under the revised law. The GPPH (Global Patent Prosecution Highway*) has been launched since January 2014, 1.
1 Request for examination
Within 5 years from the international filing date (filing date) or from the direction of the Commissioner of the Patent Office2 months* You must file a request for review by the earliest of these dates (Article 44 of the Act). In addition, before the law revision, in the case of amended examination, it was possible to delay the request for examination depending on the application status of US, EP, etc., but this has been abolished under the revised law.
2 Screening details
·Novelty
・Inventive step *The standards for determining inventive step have been raised due to the 2013 law revision.
·Usefulness
3 Grace Period
Publication in the following cases will not be considered for novelty (Article 24 of the Act):
a) Published within 12 months of the filing date of the complete application;
b) When the application is submitted within 12 months of publication in an academic organization.
c) When the application is filed within 12 months from the disclosure of the invention at an “approved exhibition”
d) The application is filed within 12 months of the public exploitation of the invention for reasonable testing purposes (only if the nature of the invention reasonably requires such exploitation).
(2) When the application is filed within 12 months from the date of disclosure without the consent of the patentee or patentee
(3) All disclosures to government agencies are not considered.
correction
1. Timing of correction
Amendments can be made at any time after application and before approval.
2. Scope of correction
Addition of new matters is not permitted. Additionally, amendments to the specification after approval will not be allowed if the claims are expanded as a result of the amendment. However, for a period of three months after publication, it is possible to file a divisional application with claims that fall outside the scope of the allowed claims.
Acceptance deadline
An application will be invalid if it is not formally granted within 12 months from the date of the first examination report (Article 142, Regulation 13.4(1)(a)). (This period was shortened from 2013 months due to the 21 law amendment.)
Objection
It is possible to file an opposition within three months from the date of publication of the patent grant (Article 3 of the Act).
reexamination
The patentee or a third party can request reexamination after the patent has been registered. Patent owners or applicants for reexamination who are dissatisfied with the reexamination decision can appeal to the federal court.
Registration
a) The term of a standard patent is within 20 years, and the term of a medical patent can be extended for up to 5 years.
b) The term of the patent of addition is bound by the term of the main patent. In the case of pharmaceutical patented inventions, the term can be extended regardless of whether the term of the main patent is extended.
innovation patent
Applications for new innovation patents ended on August 2021, 8. Existing innovation patents and innovation patents with filing dates on or before August 25, 2021 are valid until the expiration of a maximum period of eight years from the filing date.
Additionally, the following procedures will be possible after August 2021, 8.
(2021) Split innovation patent application from a parent application filed before August 8, 25
(2021) Change from standard patent application to innovation patent application before August 8, 25
design system
Type of design
There are two types of designs:
- 1. Regular design
- 2.Multiple designs
・Only applications that fall under any of the following can be submitted as one application.
- a) One design for one article
- b) One design common to multiple articles (knife and fork set, etc.)
- c) Multiple designs related to one article
- d) Where multiple articles belong to the same class of the Locarno Agreement classification, multiple designs related to them;
Target of protection: Shape, external shape, pattern, and decoration of articles
Not subject to protection: Items whose texture, material, and size are not determined, and continuous patterns of one or more units
(1) Partial design
Designs are considered to relate to the overall appearance of a product, and design protection cannot be applied to only a part of an article. However, it is possible to use the Statement of Newness and Distinctiveness to describe the characteristic shape of a product as a feature of the design. Additionally, although it is not permitted under the Design Act, it has been a common practice to represent non-characteristic parts with broken lines.
(2) Non-physical designs and “active state” designs
App icons and GUIs are not physically applied to a specific item, but appear temporarily on the product screen. Currently, many GUIs are registered and published on the database. However, it is highly likely that the Australian Intellectual Property Office will not certify this as falling outside the definition of a "design", and in that case, even if it is registered, it will be considered a valid design right and cannot be exercised by others. I can not do.
Application route
It is possible to apply via the Paris route. The priority period is 6 months from the filing date.
Documents required for application
1. Application form and drawings (Documents must be prepared in English.)
*Photos, digital images, and samples (limited to those that can be easily placed on a flat surface and easily saved with other documents) may be submitted in place of drawings.
2. Documents to be submitted that are not required but are good to have
a) Characteristic description
b) Prior art documents (if known at the time of filing)
c) A brief explanation of how to use and function the product.
Registrable designs
Designs that have novelty and distinctiveness
・Prior reference criteria must be published worldwide or used in Australia.
◇Grace period
A 2022.3.10-month grace period was introduced by the revised Design Law that came into effect on March 12, XNUMX.
・The application must be filed* within 12 months of the first disclosure of the design
(*In the case of priority claim, the filing date is based on the priority date.)
・The first disclosure of the design is by the designer, the holder, his successor, a person authorized by the designer or the holder, or the design has been plagiarized.
・Publication through design registration
・Disclosure by foreign offices and international organizations (WIPO)
*Applies to applications filed on or after 2022.3.10 or whose priority date is on or after 2022.3.10
*For disclosures made before March 2022.3.10, 12, the XNUMX-month grace period will not apply, but the existing provisions below will apply.
- Only if a design application is filed within six months from the date of first publication or use of the design, it will not be considered as a criterion for determining novelty and distinctiveness.
・Publishing or using a design at an exhibition as prescribed by the regulations (disclosing or using a design in circumstances prescribed by the regulations with the consent of the registered owner of the design or the registered owner's previous title holder)
・Unintentional disclosure or use (disclosure or use of a design by the registered owner of the design or another person who has derived or acquired the design from the registered owner's previous owner) without the consent of the registered owner of the design; use)
Application publication
There is no application publication system.
However, the design applicant must file a request for publication or registration within six months from the filing date (or priority date). If neither request is made, the application will cease to exist.
Examination
There is no substantive examination, and if the formality examination is satisfied, it will be registered.
Furthermore, in order to prove the registered design, a substantive examination can be requested after registration. (Design Law Articles 63 and 64) In that case, novelty and distinctiveness will be examined.
Objection
There is no objection system.
Registration
The validity period is 5 years from the filing date. The maximum period is 10 years from the filing date if you apply for an extension. However, if the application date is before June 2004, 6, the maximum period is 17 years from the filing date.
Exercise of rights
Before a design right holder can exercise his or her rights, the design application must be registered, substantively examined, and certified.
Others
The related design system and secret design system are not adopted.
It is not a party to the Geneva Amendment of the Hague Agreement on the International Registration of Industrial Designs.
trademark system
Types of trademark registration
Protection is available for goods, services, collective marks, certification marks, and defensive marks.
Types of trademarks include word trademarks, figure trademarks, symbol trademarks, three-dimensional trademarks, combination trademarks, sound trademarks, and scent trademarks.
We use the one-trademark, multiple-classification system.
Application route
Applications can be made via the Paris route or the Madpro route.
Documents required for application
- 1. Application form (applicant address and name, international classification of goods and services)
- 2. Trademark representation: English translation of foreign words and transliteration of non-Roman characters in the trademark
- 3. A clear explanation is required for shape, sound, smell, and color trademarks.
Application publication
None
Examination
If the formal requirements are met, a substantive examination will be conducted regarding distinctiveness and reasons for non-registration.
There is no review request system.
Acceptance deadline
Applications must be allowed within 15 months of the first office action. (Can be extended for 6 months upon request)
Objection
If there are no reasons for refusal in the substantive examination, the application will be announced. You can file an objection within three months from the date of publication. It will be registered if there is no objection or if the objection is not established.
Registration
It will be registered if the registration fee is paid within 6 months after the publication.
Non-use cancellation system
If a trademark is not used for three consecutive years after registration, it will be subject to non-use cancellation.
Comparison of patent systems between Australia and New Zealand
| Australia | New Zealand | ||
| treaty of paris | 〇 | 〇 | |
| WTO membership | 〇 | 〇 | |
| PCT | 〇 | 〇 | |
| EPC | × | × | |
| survival period |
Starting date | (Domestic patents) Application date of complete specification, (International applications such as PCT) International filing date. | |
| period | (Normal application) 20 years, (Additional patent) Remaining period after the main patent | ||
| Extension | None | None | |
| Unique patent system | Additional patents (improvements of the main patent). | ||
| Inventions that cannot be patented | Biological methods for creating humans and generations. Inventions that violate public order and morals. A substance that can be used as food or medicine. Mere mixture of known substances. A method of producing a substance that is simply a mixture. Plans, rules and methods of accomplishment for mental activities, playing games or doing business. | Mere information (work systems, document storage methods, mathematical formulas, arrangement of words and symbols), discoveries, and the treatment of people. | |
| Objection | March | March (1 month extension possible) | |
| Obligation to perform | Three years have passed since the patent. | Three years have passed since the patent. | |
Reference: General Incorporated Foundation, Economic and Industrial Research Council, Patent News, Published March 28, 3
Australian Patent Minimum Required Fee and Pension (Effective Date: December 1, 2012)
| Application fee | paper | AS$470 |
| Electronic | AS$370 | |
| ・Examination request fee AS$490 *Australian Patent Office is IPER Examination request fee when preparing (International Preliminary Examination Report) AS$300 ・Patent issue fee AS$250 |
||
| Pension (patent fees, etc.) | ||
| 1st year | - | |
| 2nd year | - | |
| 3rd year | - | |
| 4th year | - | |
| 5th year | AS$300 | |
| 6th year | AS$300 | |
| 7th year | AS$300 | |
| 8th year | AS$300 | |
| 9th year | AS$300 | |
| 10th year | AS$300 | |
| 11th year | AS$500 | |
| 12th year | AS$500 | |
| 13th year | AS$500 | |
| 14th year | AS$500 | |
| 15th year | AS$500 | |
| 16th year | AS$1,120 | |
| 17th year | AS$1,120 | |
| 18th year | AS$1,120 | |
| 19th year | AS$1,120 | |
| 20th year | AS$1,120 | |
| 21st year | AS$2,300 | |
| 22nd year | AS$2,300 | |
| 23rd year | AS$2,300 | |
| 24th year | AS$2,300 | |
| 25th year | AS$2,300 | |
| Duration of patent right | 20 years from the patent date | |
Reference: Patent Office Annual Patent Administration Report
Patent attorney advisor Minoru Goto
