table of contents
Basic Information
Country name: Republic of the Philippines
Capital: Manila
Area: 298,170 square kilometers (approximately 8% of Japan). There are 7,641 islands.
Population: Approximately 1 people (903 Philippine Census)
Accession treaties: Paris Convention, Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), WTO
Patent Office HP:http://www.ipophil.gov.ph/
News published by the Patent Office from time to timeplease use this form.
Patent law
Basic Information
Language: English or Filipino
Items excluded from protection (Article 22 of the IP Law):
- ● Discovery, scientific theory and mathematical methods and certain pharmaceutical products*
- ● Performing mental acts
- ● Plans, rules and methods for entertainment or business activities.
- ● Computer program
- ● Methods for treating the human or animal body through surgery or therapy, and methods for diagnosing the human or animal body.
- ● Plant varieties, animal varieties and essentially biological methods of plant and animal production.
- ● Aesthetic creations
- ● Anything that violates public order and morals.
*Specified drug products
…merely the discovery of a new form or property of a known substance that does not result in an improvement of the known efficacy of the substance, or merely the discovery of some new property or new use of a known substance; or Merely the use of known methods. However, this does not apply if the known process is capable of producing a new product containing at least one new reactant.
Duration (Article 54 of the IP Law): XNUMX years (no system for extending the duration)
No priority examination/accelerated examination system
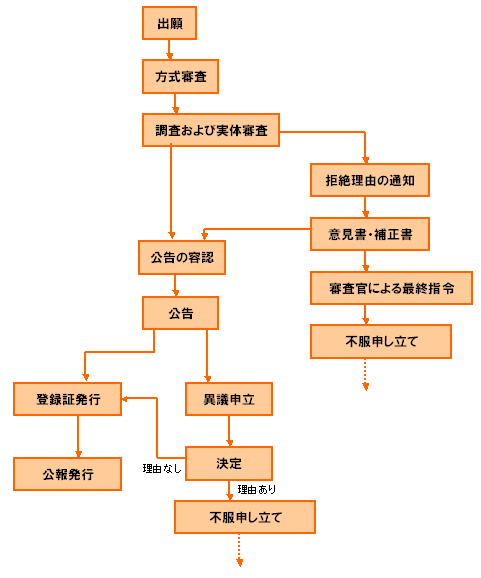
Process from application to registration
Disclosure that will not be disadvantageous (Article 25 of the IP Law)
Below 1. and 2. If the following conditions are met, the disclosure of the following information will not be grounds for lack of novelty.
- 1. Disclosure of information contained in an application during the 12 months preceding the filing date or priority date.
- 2. The above application applies if:
(a) The disclosure was made by the inventor.
(b) the disclosure is made by the Intellectual Property Office, and
a was described in another application filed by the inventor and should not have been disclosed by the Intellectual Property Office, or
b.It is stated in an application filed without the inventor's knowledge or consent by a third party who obtained the information directly or indirectly from the inventor.
(c) the disclosure is made by said third party;
Publication (Article 44 of the IP Law)
Published 18 months after the filing date or priority date.
Published along with a research document that cites documents describing prior art.
Request for substantive examination (Article 48 of the IP Law)
Within 6 months from the date of publication.
correction
*Refer to the Intellectual Property Information Data Bank website for emerging countries etc.
A patent application can be amended at the examination stage if it does not include new matters (Article 49 of the IP Law).
The response period is usually 2 months.
Can be extended up to 929 times. However, the total of the initial response period and the extension period must not exceed six months (Rule XNUMX). Extension fees are required.
divisional application
*Refer to the Intellectual Property Information Data Bank website for emerging countries etc.
- A divisional application may be filed in a pending application before the parent application is withdrawn, abandoned, or granted a patent. However, the condition is that the content does not exceed the content of the parent application. (Rule 611)
- Division of non-selected inventions after a directive in violation of unity shall be made within 4 months from the issuance of the directive or within an additional period not exceeding 4 months (Article 38 of the IP Law)
Obligation to implement (Article 94 of the IP Law)
3 years from the date of registration or 4 years from the date of application, whichever is later. Failure to do so by this later date will result in cancellation of non-use.
Change application (IP Law Article 110)
A patent application can be converted into a utility model registration application at any time before a patent is granted or rejected (a utility model registration application can also be converted into a patent application).
Can be changed only once.
Prohibition of parallel applications (IP Law Article 111)
It is not possible to file two applications, one for utility model registration and one for patent, for the same subject matter.
HPP
PPH is possible with JPO (Japan), USPTO (USA), EPO (Europe), and KIPO (Korea).
*JPO will be fully implemented from March 2021, 3.
*EPO will be fully implemented from July 2020, 7.
For JPO-PPH application instructions, please refer to the Japan Patent Office website.
“Application Procedures to the Intellectual Property Office of the Philippines regarding the Patent Prosecution Highway Pilot Program between the Intellectual Property Office of the Philippines (IPOPHIL) and the Japan Patent Office (JPO)” (tentative translation)
URL:https://www.jpo.go.jp/e/system/patent/shinsa/soki/pph/document/guideline/philippine_ipophl_ja.pdf
Statistics
*Refer to the Philippine Patent Office website
| Number of applications | ||||
| Years | PCT application | National application (Resident) |
First country application for foreigners (Non-Redident Direct) |
Total |
| 2015 | 2856 | 293 | 190 | 3339 |
| 2016 | 2609 | 248 | 243 | 3100 |
| 2017 | 2559 | 284 | 243 | 3086 |
| 2018 | 2943 | 469 | 550 | 3962 |
| 2019 | 3223 | 434 | 367 | 4024 |
*Number of applications in the third quarter of 2020 (July-September): 7% decrease compared to the same period last year.
| Number of registrations | ||||
| PCT application | National application (Resident) | Foreigner first country application (Non-Redident Direct) | Total | |
| 2015 | 1875 | 24 | 130 | 2029 |
| 2016 | 1837 | 31 | 123 | 1991 |
| 2017 | 1420 | 18 | 99 | 1537 |
| 2018 | 2085 | 29 | 565 | 2679 |
| 2019 | 1191 | 35 | 101 | 1327 |
*"Statistical information on patents and utility models obtained from the ASEAN Industrial Property Database" (March 2023, Japan External Trade Organization (JETRO) Bangkok Office, Intellectual Property Department)
URL:https://www.jetro.go.jp/ext_images/world/asia/asean/ip/pdf/report_202303_asean.pdf
*Applies to patents registered in 2022.
*Local refers to applications that are not classified into the PCT route or Paris route.
| All cases | 6.0 years (1862 cases) | |
| Applicant nationality | The Philippines | 5.0 years (65 cases) |
| Outside the Philippines | 6.0 years (1797 cases) | |
| Application route | PCT route | 6.2 years (1626 cases) |
| paris route | 3.8 years (156 cases) | |
| Location | 5.1 years (80 cases) | |
*2019-2021. See JETRO materials above, pages 122-126.
Patent related fees
URL: https://www.ipophil.gov.ph/services/schedule-of-fees/patent-related-fees/
Amendment of enforcement regulations
Effective date: September 2022, 9.
Purpose: Streamlining administrative procedures
URL:
https://www.jetro.go.jp/ext_images/_Ipnews/asia/2022/ph/20220915.pdf
https://www.jetro.go.jp/ext_images/world/asia/ph/ip/pdf/philippines-tizai_kisoku_en.pdf
utility model law
Basic Information
Language: English or Filipino
Items excluded from protection:
⇒ Same as patent
Duration: 7 years
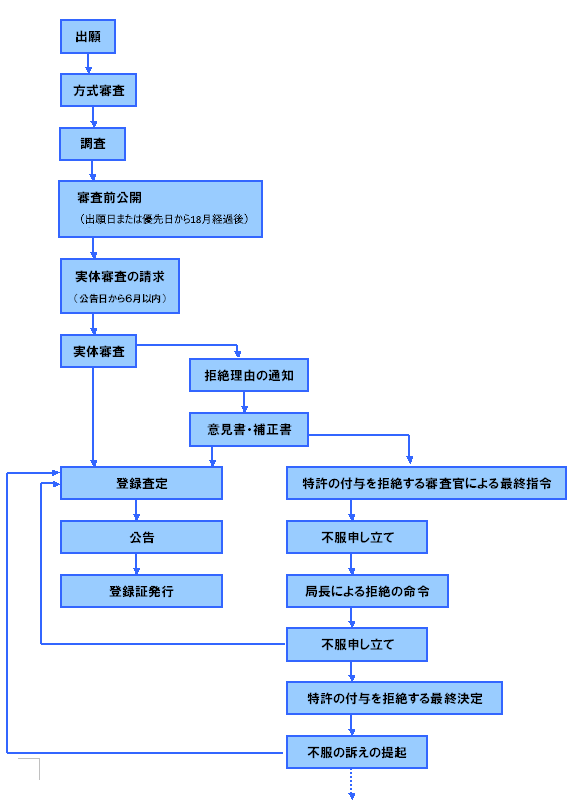
Process from application to registration
Obligation to implement (Article 108 of the IP Law used in Article 94)
3 years from the date of registration or 4 years from the date of application, whichever is later. Failure to do so by this later date will result in cancellation of non-use.
Special provisions (IP Law Article 109)
・If it is novel and has industrial applicability, it can be registered as a utility model (inventive step is not a substantive requirement).
・No substantive examination (formality examination only).
・No application publication system (however, public announcement will be made after registration).
Statistics
*Refer to the Philippine Patent Office website
| Number of applications | ||||
| Years | National application (Resident) | Foreigner first country application (Non-Redident Direct) | Total | |
| 2015 | 767 | 46 | 813 | |
| 2016 | 1102 | 46 | 1148 | |
| 2017 | 1332 | 62 | 1394 | |
| 2018 | 2080 | 66 | 2146 | |
| 2019 | 2141 | 86 | 2227 | |
*Number of applications in the third quarter of 2020 (July-September): 7% decrease compared to the same period last year.
| Number of registrations | ||||
| National application (Resident) | Foreigner first country application (Non-Redident Direct) | Total | ||
| 2015 | 489 | 38 | 527 | |
| 2016 | 555 | 35 | 590 | |
| 2017 | 504 | 27 | 531 | |
| 2018 | 1052 | 61 | 1113 | |
| 2019 | 969 | 23 | 992 | |
*"Statistical information on patents and utility models obtained from the ASEAN Industrial Property Database" (March 2023, Japan External Trade Organization (JETRO) Bangkok Office, Intellectual Property Department)
URL:https://www.jetro.go.jp/ext_images/world/asia/asean/ip/pdf/report_202303_asean.pdf
*Applies to utility models registered in 2022.
*Local refers to applications that are not classified into the PCT route or Paris route.
Average period from application date to registration date
| All cases | 9.1 years (1134 cases) | |
| Applicant nationality | The Philippines | 8.6 years (1057 cases) |
| Outside the Philippines | 15.6 years (77 cases) | |
| Application route | PCT route | 33.1 years (18 cases) |
| paris route | 14.9 years (31 cases) | |
| Location | 8.5 years (1085 cases) | |
*2019-2021. See JETRO materials above, pages 138-142.
Utility model related fees
URL: https://www.ipophil.gov.ph/services/schedule-of-fees/utility-model-industrial-design/
Amendment of enforcement regulations
Effective date: September 2022, 9.
Purpose: Streamlining administrative procedures
URL:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1SGU-OvSLEasCzKhC7tt0dkUkIARYquWd/view
https://www.jetro.go.jp/ext_images/_Ipnews/asia/2022/ph/20220915.pdf
https://www.jetro.go.jp/ext_images/world/asia/ph/ip/pdf/philippines-tizai_kisoku_en.pdf
Design law
Trends in the number of applications and registrations (2015-2019) *See Philippine Patent Office website
| Number of applications (cases) | Number of registrations (items) | |||||
| Years | overseas resident | domestic citizen | Total | overseas resident | domestic citizen | Total |
| 2015 | 555 | 530 | 1,085 | 453 | 430 | 883 |
| 2016 | 516 | 972 | 1,488 | 483 | 532 | 1,015 |
| 2017 | 666 | 727 | 1,393 | 555 | 955 | 1,510 |
| 2018 | 645 | 877 | 1,522 | 896 | 804 | 1,700 |
| 2019 | 612 | 1,019 | 1,631 | 675 | 731 | 1,406 |
Duration:
5 years from the filing date
(However, it may be renewed for no more than two consecutive five-year periods by paying a renewal fee.)
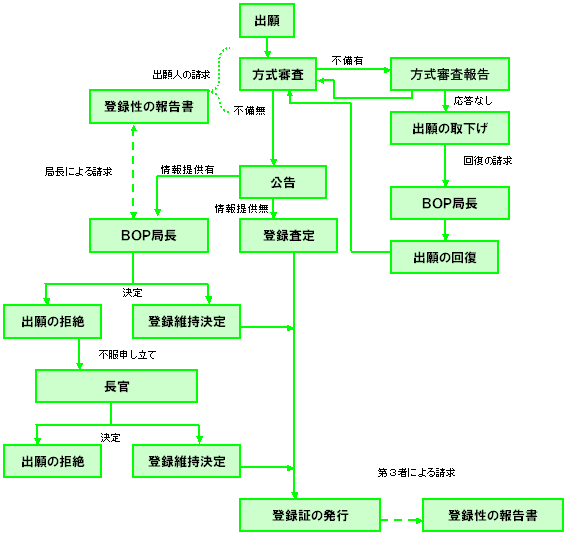
Process from application to registration:
Trends in the number of applications from 2017 to 2021
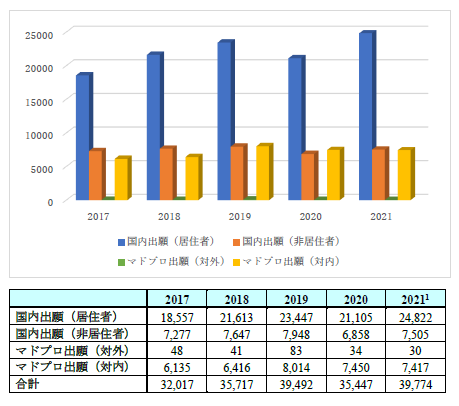
Source: Survey on the current status of trademark system and operation in the Philippines, commissioned by the Japan Patent Office
(March 2022, Japan External Trade Organization Bangkok Office)
Average review period (as of the end of October 2021)
Direct application: 4.95 months
Madpro application: 3.02 months
distinctive system
1. Submission of declaration of use
- Use of trademark is not required as a requirement for application (adoption of registration principle)
- A “Declaration of Actual Use” and evidence of use must be submitted to IPOPHL within the following deadlines:
① Within 3 years from the application date
②Within 5 year from the day 1 years have passed since the registration date
③Within 1 year from the renewal date
④Within 5 year after 1 years have passed since the renewal date
→If you do not submit it, your registration will be cancelled.
2. Disclaim system
If a part of the trademark contains a word that lacks distinctiveness or is offensive to public order and morals, and registration would be permitted without the element, the applicant waives the exclusive right to the element. You can receive registration by declaring this.
This disclaimer can be made voluntarily at the time of filing, or it can be made at the request of the examiner in OA.
3. outlet system
Even if there is a similar prior trademark, the reason for refusal due to the existence of a similar prior trademark can be overcome by submitting a letter of consent from the right holder of the prior trademark to obtain registration. .
Although it is left to the examiner's discretion whether or not to permit the use of a concentrate letter, it is said that progress is being made in the direction of respecting the consent of the right holder of the prior trademark.
4. Priority examination system
Normally, the substantive examination of applications is conducted in the order in which the formality examination has been completed and the filing date and application number have been set.
Applications that meet certain requirements can be examined preferentially, regardless of the filing date and application number, provided that the examiner has the consent of the applicant.
→Example of “application that meets certain requirements”
①Re-application for a trademark that was canceled due to non-compliance with renewal procedures
②Re-application for trademark canceled due to non-submission of declaration of use
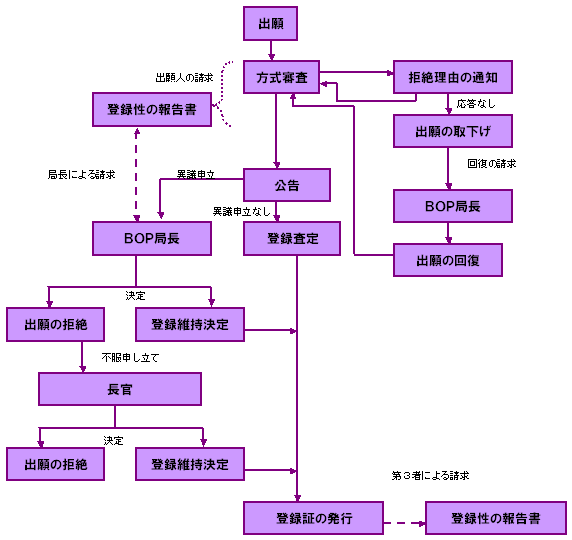
Process from application to registration: